Twinnings
DigitalHealthEurope is funding a Twinning Scheme which directly supports the replication and scaling up of successful and highly impactful digital health and care solutions in Europe.
Two calls for Twinning applications have been organised so far. Learn more about how the concept of twinnings works and what can and has already been achieved with the aid of this instrument.
What are Twinnings?
Twinnings are a mechanism for facilitating the transfer and implementation of digitally-enabled innovative practices from one region to another. The approach has been successfully tested in a number of EU projects and studies, including the ScaleAHA study.
The region that offers the innovation is called originator, and the implementing region is the adopter. In some cases, an external facilitator may be needed. Funded activities include the ventures needed to carry out the twinning (e.g. organising hosting meetings or technical groups, and financing travel expenses, licenses, or fees for professional services). Twinnings will typically last for a whole year.
Aim: to de-risk investment in digital innovative ICT solutions by financing the exchange of knowledge and good practice in digital health solutions with high potential for replicability and scaling up
Roles: originator & adopter of the innovative practice, facilitator
Funding scope: activities necessary to carry out the twinnings (e.g. hosting meetings, technical groups, travel expenses, licenses, fees for professional services not covered)
Timeframe: typically up to one year
Format: twinning applications; award contracts with agreed activities and deliverables; regular reporting
Twinnings in DigitalHealthEurope
DigitalHealthEurope is funding a twinning scheme that supports the Digital Single Market’s three priorities for the Digital Health and Care Innovation initiative:
- citizens’ secure access to and sharing of health data across borders
- better data to advance research, disease prevention and personalised health and care
- digital tools for citizen empowerment and person-centred care
More than 45 twinnings opportunities – between more than 90 organisations – will be organised. Funding will be provided to carry out twinning activities.
DHE has organised two Calls for Twinnings in 2019 and 2020.
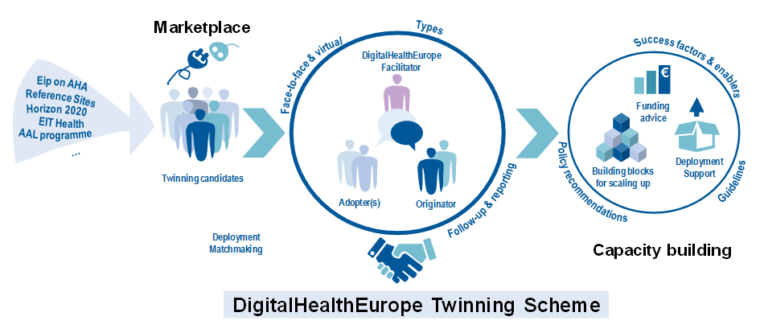
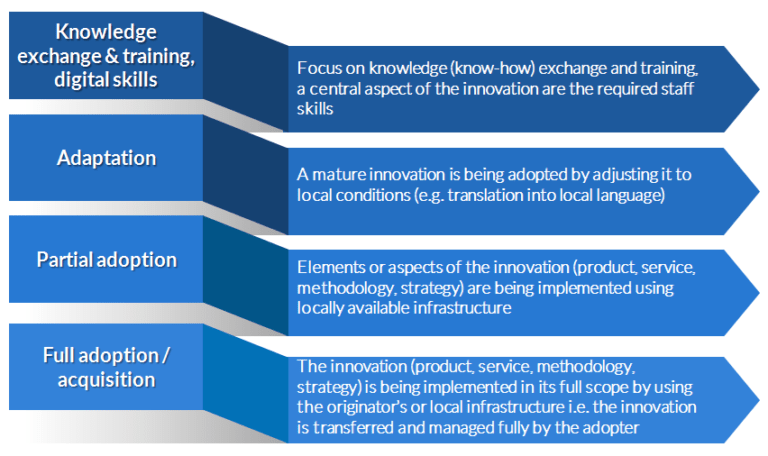
Twinning Types
Twinnings can be grouped into five types. Each type is very specific. It has different conditions for its budget, deployment timeframe, and the experts required.
The five types range from ‘knowledge exchange and training’ to ‘acquisition’:
- Knowledge exchange and training: This type of twinning mainly targets local authorities: they can be authorities that are not too experienced in EU networking, but are eager to learn from other regions in Europe. Here, the twinning provides a first step to discuss a concrete solution (product, service, methodology) and its transfer to the adopting region(s). The twinning is used to build capacity. This includes identifying staff, setting up a process roadmap, and defining expected outcomes
- Adaptation*: This type of twinning is suitable for multiple adopters (i.e., one originator can work with several adopters). The adaptation process across adopters is expected to be very similar. Well-established solutions are adapted to the local context (e.g. translating the contents of a mobile app, introducing a prevention programme).
- Partial adoption: This type of twinning is suitable for local authorities that wish to implement aspects of an originator’s innovative approach. Twinnings that perform a partial adoption will have to provide concrete evidence on the potential impact of the adoption, as well as the reasons why a full adoption is not possible (e.g. because they have different healthcare systems, organisations, or reimbursement schemes).
- Full adoption / acquisition: This type of twinning mainly targets local authorities with well established relations with other authorities in Europe (e.g. through memorandums of understanding, past EU project partnerships, etc.) and who have already planned collaboration on a specific topic/solution. The twinning aims to achieve a full adoption of the solution in the adopting region(s) using local infrastructure (including adaptation) or the originator’s infrastructure (via acquiring or licensing it using appropriate business models).
Examples of types of exchange
*The Second DHE Call for Twinnings (February – May 2020) excludes “Adaptation” as a potential Twinning type.
Twinning Success Stories
The concept of twinnings has already been succesfully employed in several project and studies. DigitalHealthEurope would like to share some twinning success stories from regions around Europe which have been previously funded under the Scale AHA study twinning scheme.
Health Center Zagreb and the Regional Ministry of Health of Andalusia took part in a twinning as part of the 2016 ScaleAHA twinnings. The aim of the twinning was for Zagreb to learn about the Diraya system and implement elements of it in the region. Zagreb wished to twin with advanced regions in order to find digital solutions related to Active and Healthy Aging that could be implemented in the region, and to learn from experiences of Reference Sites that have successful eHealth strategies in place. Andalusia’s more than 20 years of experience in eHealth systems development and its elaborate operating system Diraya made the Andalusian Reference Site the excellent candidate for twinning. Zagreb and Andalusia submitted a twinning application for knowledge transfer focusing on the Diraya system.
Diraya is a comprehensive system that supports the Andalusian electronic medical record system. The conceptual model and the technological architecture of Diraya have raised enormous interest in other health administrations thanks, among other things, to its cutting-edge services such as the electronic prescription or the centralized appointment system.
Following the twinning, Health Center Zagreb organised a series of co-development workshops with primary care physicians and ICT service providers in order to find the best ways to implement the desired elements in the Croatian healthcare ecosystem. As a result of these sessions, a set of modules which were added to the existing service Zdravlje.net were created and carefully implemented by conducting a series of pilot-projects. This proved to be a highly successful approach, resulting in opening up new communication channels between citizens, health care providers and health care workers. Healthcare services for complex patients have been improved based on examples from Andalusia health services with the expected significant impact on the quality of health service delivery.
One of the most challenging, yet rewarding results was the development of the E-consultation module informed by the Diraya system and the experience of Andalusia. E-consultation is a cross-specialty communication tool built on an existing inter-professional communication model Zdravlje.net PRO used in GP practices. This digital service fosters collaboration between cure and care sectors and provides multidimensional approach to managing patients. Patients can receive hospital specialist recommendation for managing a specific health issue based on GP-hospital specialist multidisciplinary interaction. This recommendation then transforms to time and financial savings for the patient and the healthcare system, optimised care patterns, and could help improve quality of care and health outcomes.
“The twinning with Diraya informed the development of a number of modules which have since been added to the existing Zagreb service portfolio. Most notably, an e-consultation module was developed based on the twinning results” – Antonija Balenović, Director of Health Center Zagreb
With the current level of scale-up and through the increasing public demand, the transferred services could reach up to 350 000 patients and there are indications that some solutions could soon be implemented on national level, potentially impacting millions. We believe that the key to more adaptive policy on digital health solutions is to showcase the benefits of the solutions in small-scale pilots and communicate well on different levels to both create the public demand for the solution and facilitate the adoption of enabling policy.
A delegation from Andalusia took part in a twinning study visit to Scotland (12th – 13th January 2017), as part of the 2016 ScaleAHA twinnings. Both regions are recognised as 4-star Reference Sites of the European Innovation Partnership on Active and Healthy Ageing (EIP on AHA). The visit focused on the Scottish platform Living it Up (LiU), aimed at people over 50 years to promote active and healthy aging.
The Regional Ministry of Health of Andalusia was developing the “Promotion of Active and Healthy Aging through Digital Solutions” project, funded by the European Regional Development Fund ERDF, with the aim of launching a digital platform in Andalusia similar to the Scottish one, hence the great interest in this visit.
On January 12th, the visit started at the NHS24 site, Scottish public organization for telehealth and telecare, in Cardonald, where the LiU services and procedures were presented, including health advice and information.
LiU is a digital service in which allows to access and share local information to adopt a happy and healthy lifestyle. Through the LiU platform, the main challenge of the Scottish Government is to motivate people to acquire and voluntarily choose a lifestyle that provides physical and mental well-being. Thus, the motto of the Scottish platform can be summarised in the following expression: “Be healthier, be happier and feel more secure”.
The platform has been developed with the participation of more than 3,000 people, and its design has involved professionals from the University. Among its users, more than 55% are people with at least one chronic disease, interested in the management of their disease and the connection with their environment. Another 35% have had a recent health incident. Therefore, the users’ “path” in the services was analysed to consolidate the platform, seeking to respond to the demands of these user profiles. The LiU platform is fed by information from the Local Services Database of Scotland (ALISS) updated by the municipalities that have committed to it. The platform is currently active in several geographic areas of Scotland.
Among the services available on the Scottish platform are “smartcare” applications, designed to record and share relevant information on health and social care of each person, as well as the possibility of managing the registration of appointments. The social and health information generated through the application meet the confidentiality and security requirements.
One of the aspects to highlight in the process of implementing the Scottish platform is the evaluation carried out through a study developed over 12 weeks with continuous monitoring of two profiles: people to whom the platform was offered and who entered it and another control group to which the platform was not offered. The group that entered the platform used 3 times more health services; in addition they have had an added value when detecting accessibility gaps to social services.
On January 13th, the visit continued to the NHS centre in the geographical area of Lothian-Forth Valley to learn about the work at the local level on the Living it Up platform. Platform managers commented how promotion and dissemination is carried out at all levels, through direct contact with health professionals; and through digital literacy strategies developed in collaboration with voluntary associations and the third sector. Among the challenges for the LiU platform were the connectivity between corporate services and other services available in the community; stability in work teams due to funding issues; the capture of the target population of the platform; the resistance on the part of medical professionals; the improvement of the browsing experience, etc.
The final visit was to the Health Department of the Scottish Government, where the National Citizen Portal project was presented, of which the Living it Up platform is a part. The objective of this initiative is to integrate health and social resources into a single repository to provide a unique access to the user’s history of health and social services.
The Andalusian delegation had the opportunity to learn firsthand the main recommendations for the development of the digital platform of “Active and Healthy Aging” in Andalusia, including education and literacy of potential users; consulting users about their needs, expectations and demands; the commitment to participate jointly in the development of the platform; the co-design and co-production of content for the platform by the managers and the users.
Today, the Andalusian AHA digital platform is actively running at www.enbuenaedad.es. There are more than 30000 registered users and it is evolving thanks to the co-creation process of its design. The visit to Scotland helped not only to learn what went right but also to share potential pitfalls, accelerating the development process in Andalusia.
The MACVIA-France Network and initially ten adopters took part in the 2016 ScaleAHA twinnings: Campania (IT), Catalonia (ES), Porto (PT), Olomouc (CZ), Lodz (PL), Medical Delta (NL), Northern Ireland (GB), Piemonte (IT), Southern Denmark (DK) and GARD Regional Network Turkey (TR).
The aim of the twinning was to introduce the French MASK-air app (formerly Allergy Diary) to the other regions and especially enroll elderly people in order to get insight into characteristics and treatment of rhinitis and asthma multi-morbidity in this group. The longer-term objective was to make individualised and predictive medicine available for rhinitis and asthma multi-morbidity of older people. Moreover, the percentage of adults and elderly that are able to use the app were to be examined.
MASK-air collects information on the symptoms, the disease type, the impact and the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Initially it has been used in 15 different European countries adapted to the different languages, cultures and the legal system. Due to its success it is available today in 23 countries and 17 languages with 26.000 registered users.1
The twinning started with ten European adopters. Today the app is deployed by 22 Reference Sites or regions across Europe and 885 patients have been enrolled in the twinning. The results show that a major problem in the treatment of allergy is the patient’s compliance with the prescribed treatment. Therefore, an expansion of self-management strategies is suggested. Moreover, results show that a patient-centred approach should be used for education strategies.
Rhinitis and asthma affect the sleep of patients. MASK-air can evaluate sleep impairment. For future use the app is being developed to include questions that relate to sleep. Furthermore, the data collected by the app shall be correlated with the amount of allergen exposure and pollution.2
1 Bousquet J, Agache I, Aliberti MR, et al. Transfer of innovation on allergic rhinitis and asthmamultimorbidity in the elderly (MACVIA-ARIA) EIP on AHATwinning Reference Site (GARD research demonstrationproject). Allergy. 2018;73:77–92; doi.org/10.1111/ all.13218, p. 83.
2 Ibid. p.90.
Campania early cluster joined the EIP on AHA community in 2013. The initial core partners were welcomed in the different Action Groups, that provided guidance and examples of how becoming involved in collaborative activities might generate results to exploit at local levels (university, health system, SMEs, community). Further engagement has been progressively supported by the set-up of the RSCN, where the interaction with other EU regional clusters has been pivotal to increase the maturity and structure of Campania Reference Site (CRS). A key enabling factor has been the parallel set-up of the national network for the internationalization of the regional health systems, the ProMIS, that has been providing further elements to strengthen the regional approach, also helping to overcome local bottlenecks.
Twinnings
Campania Reference Site for the EIP on AHA participated in 5 projects of the Transfer of Innovation Twinning Support Scheme call, in order to contribute to the European scaling-up strategy of the EIP on AHA at regional level.
Campania as Adopter
MACVICA (France): Campania has been adopter from MACVIA of Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA), a multisectoral pathway for rhinitis and related multimorbidity in older adults. The ARIA initiative aims to develop an inter-professional care models (Pharmacists, GPs, Specialists) for an integrated management of patients affected by allergic rhinitis. The project is developed through a smartphone app that allows assessment of rhinitis, and uses clinical decision support system (CDSS). The goal of the scale-up in Campania is to accelerate the adoption of the tool by users through the network of local health agencies and pharmacies.
QMCI-I (Ireland): Campania has been adopter from Quick Mild Cognitive Impairment screen (QMCI), a rapid and reliable tool to distinguish normal people from subjects with MCI. The twinning with Ireland led to a multicenter study that has been aimed at validating the Italian version of the QMCI (QMCI-I) and to obtain normative data. Further study in Italian patients with MCI are ongoing, to better clarify the diagnostic properties of the QMCI-I, to be addressed by ICT supported neurologic multi-domain training.
Telerevalidatie.nl® (Netherlands): Through the Twinning support scheme, CRS developed a pilot study for the adoption of the tool of tele-rehabilitation Telerevalidatie.nl® to evaluate the adoptability of the tool in patients with Chronic Heart Failure. It is is an ICT Platform that supports rehabilitation at home, allowing the patient to receive a personalized training program with tutorial videos and to track their training progress and physical activity during all day.
MGP (Netherlands): Campania has been the adopter in a Twinning project on a digital Modular Gastrological Platform (MGP) facilitating inter-professional effort to implement a primary gastrological approach to address specific food needs. MGP focused on supporting workflows in the Primary and Secondary Care Level, grounded in capacity/knowledge building of the chef workforce.
Campania as Originator
Campania has been the Originator in a twinning scheme with CTIC Centro Tecnológico Asturias, Spain, on an innovative practice consisting of an ICT-based home monitoring system provided as a service by a private company of home care, ‘Assistenza Domiciliare per Dimissioni Protette (ADD) protection’, that allows the hospital staff to monitor the patients at home, as if the patient was still in the hospital. The data collected at the patient’s home are made available to the staff of the hospital through a web-based platform, which feeds the hospital Electronic Health Record (EHR) of the patient.
The impact
The twinning experience has been impacting the local ecosystem of health innovation in different ways:
Raising awareness about the urge to address some specific issues (ex. Polypharmacy, integrated care, education and training, empowerment, adapted physical activity etc);
Facilitating access to validated good practices that could be tailored to the local context;
Strengthening the collaborative ties with EU regions through agreements;
Identifying and exploring new avenues for sustainable development that could be pursued at local level with new, interinstitutional approaches.
The future
Joining international ecosystems brings the added value of supporting regions to enter a journey with enthusiasm and courage, facing challenges that would not be possible to address standing alone. Building a stepwise approach towards the digital transformation of health and care will bring sustainability to our health systems, by piecing together the building blocks emerging from the twinning experience into a shared vision.
Twinning Marketplace
The DHE Twinnings Marketplace is currently under maintenance
Twinning Results
The results of the two DigitalHealthEurope Call for Twinnings are available.
